In the fast-paced world of technology, terms like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and deep learning often cause confusion. I won’t lie; I was also confused by these terms in the past. So This article aims to demystify these concepts and shed light on the distinctions between them. Let’s delve into the world of AI to understand its broad definition and explore the nuances that set machine learning and deep learning apart.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence:
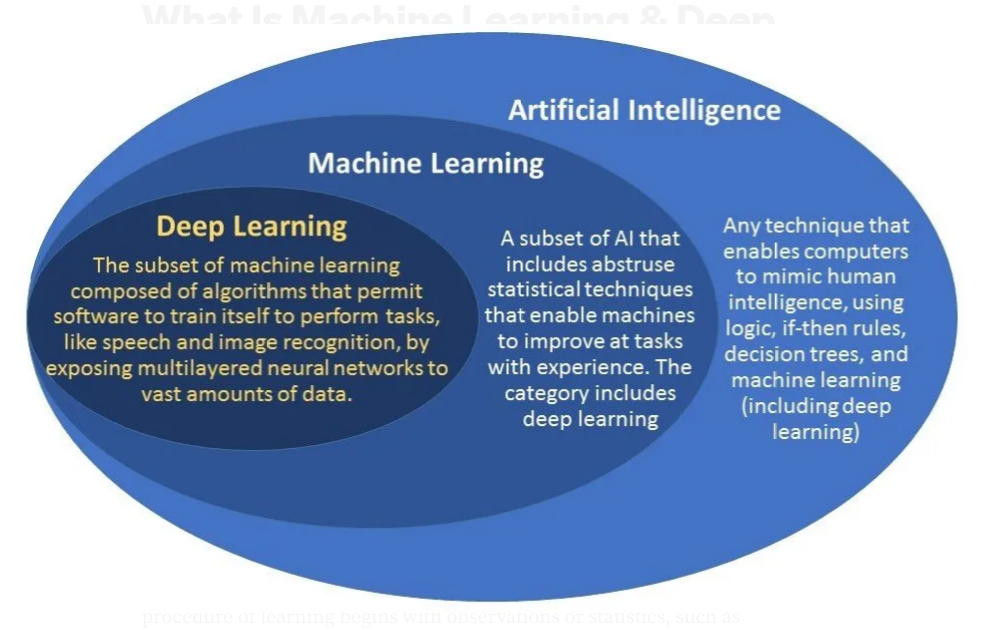
Artificial intelligence, in its broader sense, refers to machines designed to simulate human consciousness. Contrary to the futuristic image of robots with human-like abilities, AI, in practice, is employed by data scientists to address real-world issues. It acts as a technological umbrella, autonomously solving problems by mimicking human intelligence through algorithms. Take chatbots, for instance, where AI algorithms analyze customer inquiries and provide tailored responses stored within a database.
Machine Learning: A Practical Subset of AI:
Considered a subset of AI, machine learning focuses on the practical aspects of achieving the grand vision of intelligent machines. Unlike AI, machine learning doesn’t carry the connotations of creating sentient beings. Instead, it encompasses models, processes, and supporting technology used to solve problems effectively. This distinction is crucial, as machine learning serves as the driving force propelling us toward the broader goal of artificial intelligence.
There are many branches of machine learning, but the goal here is to understand globaly that machine learning is how computers learn from data. In supervised learning, computers use labeled examples to make predictions. Unsupervised learning identifies patterns without labeled data. Reinforcement learning trains a computer to make decisions by rewarding good actions and penalizing bad ones. It’s akin to teaching a computer through guidance, patterns, or trial and error.

Deep Learning: Scaling Up with Complexity:
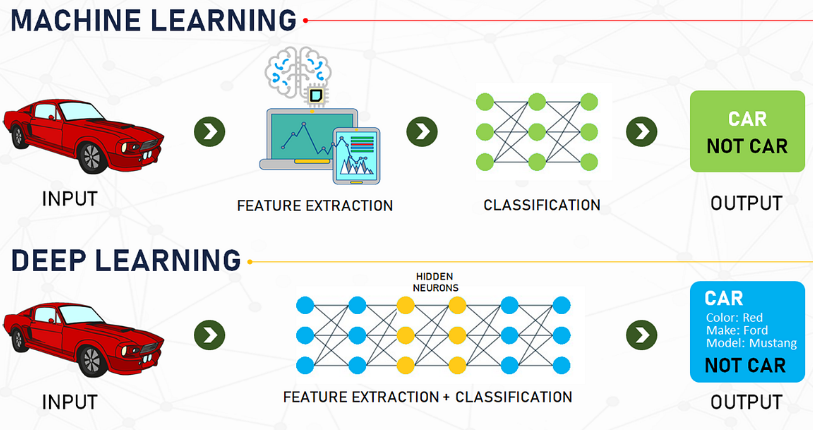
Within the realm of machine learning, deep learning emerges as a larger-scale approach involving extensive training data and intricate neural networks. Neural networks, essentially algorithms designed to find solutions with minimal error, resemble the interconnected nodes in the human brain. The pivotal difference between machine learning and deep learning lies in the number of layers these nodes pass through. As technology advances, deeper neural networks with more hidden layers become possible, leading to what data scientists refer to as deep learning.
Conclusion:
In summary, artificial intelligence represents the overarching vision of intelligent machines. Machine learning, a subset of AI, encompasses the practical processes and tools driving us towards that vision. Deep learning takes machine learning to a larger scale, involving more sophisticated neural networks, larger datasets, and robust computing power. Understanding these distinctions enables individuals to navigate the exciting and evolving field of AI, providing a foundation for building and implementing projects in this dynamic technological landscape.