Hello everyone, today we will talk about Qlik Automation, it’s a no-code tool that enables the automation of manual tasks. Instead of writing code, users combine configurable blocks that they drag and drop onto a canvas, forming a sequence of action steps from various SaaS applications, including Qlik Cloud. These steps run like a program to automate business processes, using analysis to direct the flow of data across multiple applications.
Architecture
Automations can be executed manually, scheduled, listen for webhook events, and triggered using an API endpoint. Automations are compiled into native code that runs in Kubernetes pods on Qlik Cloud.
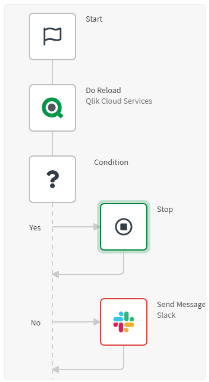
Each automation is composed of different chained building blocks to create a flow. There are three types of building blocks:
Components

The starter block is your starting point and is mandatory in every automation. It is already present on the canvas and defines the beginning of the automation process; any other block in the automation must be connected to the chain of the starter block.

Standard blocks are divided into 4 categories (Basic, List, Advanced, and Cloud Storage). Some examples of usage include:
Connectors

Qlik Application Automation offers a range of connectors. Connectors serve as a link between third-party applications and the automation. They can be used to retrieve data from a third-party application or to write data into that application.

One notable connector is the Qlik Cloud service connector, which enables connection to Qlik’s SaaS resources (apps, reloads, connections, etc.). It requires no authentication and benefits from the authorization of the logged-in user.
Execution Types

In addition to manually executing an automation, automations can be automatically executed in three different ways:
Scenarios
